1. Economics is a social science that involves the study of how individuals
A) choose among alternatives to satisfy their unlimited wants.
B) maximize their wealth.
C) develop their tastes and preferences.
D) define happiness.
2. microeconomics is concerned with the study of
A) aggregate demand.
B) the effects of government spending.
C) the effects of inflation.
D) the effects of an increase in the price of coal.
3. Economists assume people are motivated by
A) selfishness.
B) pride.
C) social justice.
D) self-interest.
4. People behave rationally when they
A) make decisions they think will make themselves better off.
B) never have regrets about their decisions.
C) make decisions based on scientifically-proved criteria.
D) follow the advice of economists.
5. "Ceteris paribus" means
A) "other things constant."
B) "making all the necessary changes
C) "invisible hand."
D) "economic man."
6. Normative economic analysis involves
A) purely descriptive statements.
B) if-then statements.
C) testable hypotheses.
D) value judgments.
7. Scarcity exists because
A) not enough resources in the past were used to develop new technologies that would have eliminated scarcity.
B) the world is too small.
C) human wants are greater than what can be produced with the limited resources available.
D) people are too greedy and refuse to share what they have with others.
8. Resources are also known as
A) minerals.
B) land and capital.
C) stocks, bonds, and other financial instruments.
D) factors of production.
9. Opportunity cost is
A) the same thing as the money price of a good.
B) the value of the next best alternative.
C) the combined value of all the alternatives not selected.
D) based on the intrinsic value of the good itself.
10. A point outside a production possibilities curve indicates
A) opportunity costs are constant.
B) that resources are being used very efficiently.
C) an output combination that can be attained only if society gets more resources or there is technological change.
D) that resources are not being used efficiently.
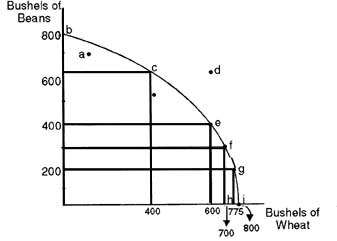
Refer to the figure above to answer questions 11-14.
11. Refer to the figure above. Which of the following points indicates efficient use of resources?
A) h
B) d
C) a
D) i
12. Refer to the figure above. The shape of the production possibility curve indicates that
A) production of both goods is characterized by increasing costs.
B) production of wheat is characterized by decreasing costs while the production of beans is characterized by increasing costs.
C) production of both goods is characterized by decreasing costs.
D) production of wheat is characterized by increasing costs while the production of beans is characterized by decreasing costs.
13. Refer to the figure above. Between points f and g, opportunity cost of another bushel of beans is
A) 2 bushels of wheat.
B)l.33 bushels of wheat.
C) 3/4 bushel of wheat.
D)l bushel of wheat.
14. Refer to the figure above. Which of the following would allow society to move to point d?
A) Concentrating production in wheat.
B) Increasing the quantity of labor.
C) Using the best land to produce wheat and the lower quality land to produce beans.
D) Producing efficiently.
15. The law of increasing relative cost is due to
A) inefficient use of technology.
B) the fact that there are always alternatives and it is costly to figure out which alternative is best.
C) the fact that resources are not perfectly adaptable for alternative uses.
D) scarcity.
16. Demand is a schedule of
A) how much of a good people will purchase at each different possible price.
B) how much of a good a person wants.
C) each possible price and the amounts people will buy when their incomes change.
D) How much of a good people will purchase at each different price and income.
17. A shift in demand occurs when
A) price changes.
B) the amount demanded changes for every price.
C) price changes and the good is a normal good.
D) time is not held constant.
18.Which of the following causes a decrease in demand for a normal good?
A) Increase in price of a substitute
B) Increase in price
C) Increase in income
D) Increase in price of a complement
19. A normal good is one for which
A) demand increases as income increases.
B) the demand curve is horizontal.
C) demand increases as the price of a substitute increases.
D) demand increases as income changes, regardless of the direction of the change.
20. A decrease in quantity demanded of a good is caused by
A) a decrease in the price of a substitute.
B) an increase in the price of the good.
C) a decrease in income.
D) a change of tastes.
21. An increase in price leads to
A) a change in quantity supplied, but we cannot tell if it would be positive or negative.
B) a decrease in quantity supplied.
C) no change in quantity supplied.
D) an increase in quantity supplied.
22. Holding supply constant, a reduction in demand leads to
A) lower prices and higher quantity supplied.
B) higher prices and lower quantity supplied.
C) higher prices and higher quantity supplied.
D) lower prices and lower quantity supplied.
23. If price increases and the quantity purchased increases, we know that
A)demand decreased.
B) supply increased.
C) supply decreased.
D) demand increased.
24. An increase in supply causes
A) price to increase.
B) quantity demanded to increase.
C) quantity supplied to increase.
D) quantity supplied to decrease.
25. Prices ration goods to
A) the people willing and able to pay the highest price.
B) the people who want the good the most.
C) the richest people.
D) the people with the lowest opportunity cost of time.
26. Minimum wage is an example of a
A) market clearing price.
B) price ceiling.
C) black market.
D) price floor.
27. The market clearing price for gasoline is $1.50, but the maximum price that can be charged is $1.29. This is an example of
A) a price ceiling that will lead to a shortage of gasoline on the market.
B) a price control that will lead to a surplus of gasoline on the market.
C) a price floor that will lead to a surplus of gasoline on the market.
D) price floor that will lead to a shortage of gasoline on the market.
28. Under rent controls
A) the quantity supplied of rental units is greater than it would be under freely competitive markets.
B) there is a shortage of rental units.
C) there is less government involvement in rental markets overall because there is a better supply of low-income housing.
D) all renters are better off than under freely competitive markets.
29. Market failures
A) encourage people to purchase more of a good than they really want.
B) are usually caused by government interference in the economy.
C) encourage businesses to produce more of a good than they really want.
D) prevent the price system from attaining economic efficiency.
30. A situation in which a market economy leads to too few or too many resources going to a particular economic activity is known as
A) destructive competition.
B) excessive competition.
C) competition.
D) market failure.
31. Markets tend to over-allocate resources to the production of a good when
A) the external costs are greater than the internal costs.
B) there are negative externalities.
C) there are positive externalities.
D) the external benefits are greater than the internal benefits.
32. Private goods are goods
A) for which the more one person has the less is available for someone else.
B) that carry a price.
C) for which price is greater than zero.
D) which are not produced by the government.
33. The free-rider problem plagues public goods because
A) once public goods are produced it is not possible to exclude free riders.
B) public goods are not produced by profit-maximizing firms.
C) the public doesn't care about public goods.
D) the government cannot refuse to serve a citizen.
34. Which of the following is not an example of a transfer payment?
A) Unemployment benefits
B) Social security
C) Welfare
D) Interest payments on government bonds
35. The marginal tax rate is defined as
A) taxes owed divided by taxable income.
B) taxable income divided by taxes owed.
C) the change in taxes owed divided by the change in taxable income.
D) the tax rate in the lowest tax bracket.
36. A family making $30,000 pays $2000 in taxes and a family making $36,000 pays $2600 in taxes. The tax rate system is
A) regressive.
B) flat-rate.
C) proportional.
D) progressive.
37. Tax incidence refers to
A) the tendency of some people to avoid paying taxes at all.
B) the distribution of tax burdens among groups.
C) determining the marginal tax rate applied to any increase in income.
D) determining who sends the taxes to the government.
38. The largest spending category for state governments is
A) health care.
B) highway construction.
C) education.
D) welfare.
39. In the market system, firms produce using the least-cost combination of inputs
A) when they don't care about producing goods of high quality.
B) when they follow carefully government regulations about production techniques.
C) because that gives the owners the most profit.
D) because the engineers in firms want to be efficient.
40. An essential characteristic of pure capitalism is
A) centralized decision-making.
B) no role for government.
C) the existence of private property rights.
D) price controls.
41. Which of the following expressions comes closest to capturing the meaning of "laissez-faire"?
A) Democracy may not be a good form of government, but it is better than the alternatives
B) Ask what you can do for your country
C) To each his own
D) The government that governs best is the government that governs least
42. In economic systems in which prices are not allowed to function as a rationing device,
A) prices are still used for incentives.
B) rationing often occurs by people waiting in lines.
C) a fairer distribution of income exists.
D) a fairer allocation of resources exists.
Answers:
1. A) choose among alternatives to satisfy their unlimited wants.
2. D) the effects of an increase in the price of coal.
3. D) self-interest.
4. A) make decisions they think will make themselves better off.
5. A) "other things constant."
6. D) value judgments.
7. C) human wants are greater than what can be produced with the limited resources available.
8. D) factors of production.
9. B) the value of the next best alternative.
10. C) an output combination that can be attained only if society gets more resources or there is technological change.
11. D) i
12. A) production of both goods is characterized by increasing costs.
13. C) 3/4 bushel of wheat.
14. B) Increasing the quantity of labor.
15. C) the fact that resources are not perfectly adaptable for alternative uses.
16. A) how much of a good people will purchase at each different possible price.
17. B) the amount demanded changes for every price.
18. D) Increase in price of a complement.
19. A) demand increases as income increases.
20. B) an increase in the price of the good.
21. D) an increase in quantity supplied.
22. D) lower prices and lower quantity supplied.
23. D) demand increased.
24. B) quantity demanded to increase.
25. A) the people willing and able to pay the highest price.
26. D) price floor.
27. A) a price ceiling that will lead to a shortage of gasoline on the market.
28. B) there is a shortage of rental units.
29. D) prevent the price system from attaining economic efficiency.
30. D) market failure.
31. B) there are negative externalities.
32. A) for which the more one person has the less is available for someone else.
33. A) once public goods are produced it is not possible to exclude free riders.
34. D) Interest payments on government bonds
35. C) the change in taxes owed divided by the change in taxable income.
36. D) progressive.
37. B) the distribution of tax burdens among groups.
38. C) education.
39. C) because that gives the owners the most profit.
40. C) the existence of private property rights.
41. D) The government that governs best is the government that governs least
42. B) rationing often occurs by people waiting in lines.
Взято с сайта: http://grandroyalinferno.tripod.com/

 Факультет экономических наук НИУ ВШЭ
Факультет экономических наук НИУ ВШЭ
Комментарии
Этот тест вышкинский напоминает
мне казалось,C
больше половины тестов уже решал (причем все в одной книге укр. автора)
ну все-таки 2 ошибки(как всегда я невнимателен)
вот.